Understanding the Basics of a Power Inverters: How Do They Convert DC to AC?
Power inverters serve as a bridge between the DC power generated by batteries, solar panels, or other sources and the AC power required by most household and industrial devices.
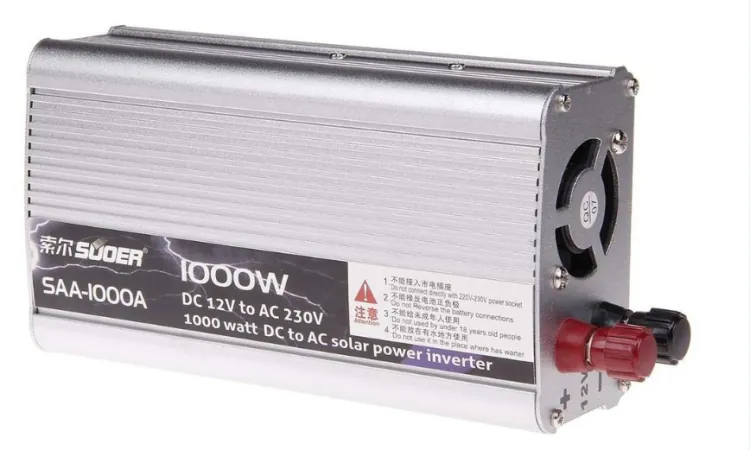

Power inverters play an important role in our modern lives by enabling the conversion of direct current (DC) into alternating current (AC). This inverter technology is essential for various applications, from powering household appliances during a blackout to facilitating the use of electronic devices in vehicles.
Introduction to Power Inverters:
Power inverters serve as a bridge between the DC power generated by batteries, solar panels, or other sources and the AC power required by most household and industrial devices. If you have a solar panel system in your house then you must be aware of that. Now, understanding how they perform this conversion is fundamental to grasping their significance.
Basic Operation:
At the heart of a power inverter is an electronic circuit that manages the conversion process from DC to AC. The key components include transistors or MOSFETs (Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor Field-Effect Transistors), capacitors, and transformers. The process involves a few stages:
Rectification: The incoming DC power is initially passed through a rectifier, which converts it into a pulsating DC. This pulsating DC consists of a unidirectional current, but it lacks the smooth waveform of AC power.
Inversion: The pulsating DC is then fed into an inverter circuit, where transistors or MOSFETs rapidly switch on and off. This switching action effectively recreates an AC waveform by producing alternating pulses of positive and negative voltage.
Filtering: The resulting AC waveform is often a square wave or modified sine wave, which may not be suitable for all devices. To address this, additional circuitry and filters are employed to refine the waveform, providing a cleaner and more stable AC output.
Types of Power Inverters:
Power inverters come in various types, classified based on their output waveform. Pure sine wave inverters produce a smooth, sinusoidal waveform similar to the grid power, making them ideal for sensitive electronics. Modified sine wave inverters, while more economical, may cause issues with certain devices due to their less refined waveform. You can find the types of power inverters in this article.
Related:- Question About Power Inverter
Applications:
Off-Grid Power Systems: Power inverters are integral to off-grid solar systems, where they convert energy stored in batteries into usable AC power for homes or businesses. But the installation cost of this system is a little bit higher till now.
RVs and Boats: Inverters enable the use of electronic devices on recreational vehicles and boats, allowing individuals to enjoy modern amenities even in remote locations.
Emergency Backup: During power outages, inverters provide a reliable source of electricity for essential appliances, ensuring continuity in critical situations. This system is suitable for places where power blackouts are more often and it also is a source of clean energy from the Sun.
Power inverters shed light on their vital role in our daily lives. From providing electricity in off-grid settings to serving as a backup power source, these devices contribute significantly to the convenience and reliability of our modern electrical systems. As technology continues to advance, power inverters will likely play an even more crucial role in shaping our energy landscape.