A Comprehensive Guide to The World of Electronic Components
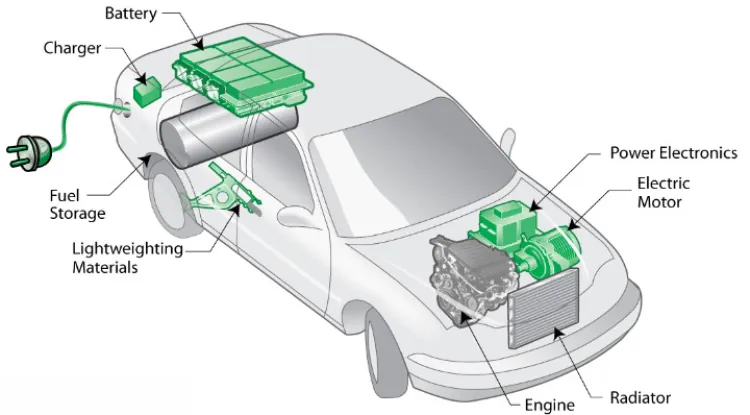
Electronic components form the backbone of every electronic device, from the smallest sensors inside your cellphone to the most sophisticated computers that can take humans to The Moon again.
In the digital realm of electronics, understanding the fundamental building blocks is essential for enthusiasts, hobbyists, and professionals alike. Electronic components form the backbone of every electronic device, from the smallest sensors inside your cellphone to the most sophisticated computers that can take humans to The Moon again. This comprehensive guide aims to unravel the intricate world of electronic components, shedding light on their types, functions, and applications.
Resistors: Resistors are the silent heroes that impede the flow of electrical current to the present circuit. They come in various types, such as fixed resistors and variable resistors (potentiometers), offering precise control over current and voltage in circuits. Its applications range from limiting current to voltage dividers and signal conditioning.
Capacitors: These components store electrical charge and release it when needed in the circuit. Capacitors are crucial for smoothing power supplies, coupling, and decoupling signals, and filtering unwanted noise. you will find a big capacitor with a ceiling fan in your room. Different types include electrolytic, ceramic, and tantalum capacitors, each with its unique characteristics.
Inductors: Inductors resist changes in current flow, storing energy in a magnetic field. They find applications in transformers, filters, and energy storage. Coils, chokes, and transformers are examples of inductive components with diverse roles in electronic circuits. For a practical experience, you can have a look inside any old TV PCB Circuit Board.
Diodes: Diodes permit current flow in one direction and block it in the other. That means the current can not take the reverse direction. From light-emitting diodes (LEDs) to rectifier diodes, they serve various functions in electronic circuits. Zener diodes maintain a constant voltage, while Schottky diodes excel in high-frequency applications.
Transistors: Generally, transistors act as electronic switches or amplifiers. With types like bipolar junction transistors (BJTs) and field-effect transistors (FETs), they enable signal amplification, switching, and signal modulation. Integrated circuits often incorporate multiple transistors for sophisticated functionality.
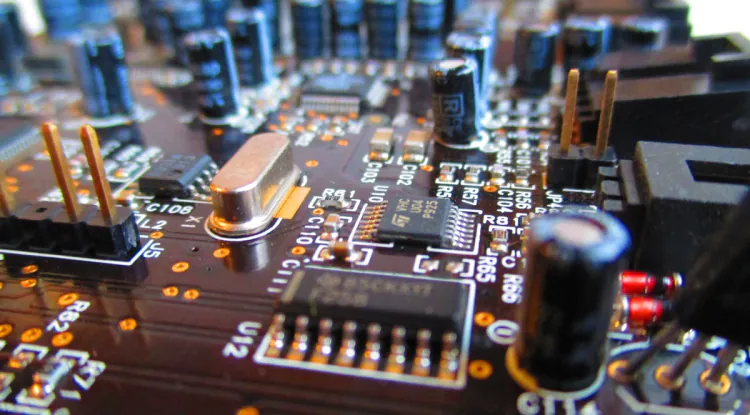
Integrated Circuits (ICs): ICs are the brains of electronic systems, housing numerous interconnected components on a single chip. If you already have a Smartphone then you already know that you spent a quite amount of money on the memory and the speed of your phone. Microcontrollers, microprocessors, and memory chips fall under this category. The miniaturization of components on ICs has revolutionized the electronics industry, enabling powerful and compact devices.
Sensors: Sensors convert physical quantities, such as temperature, light, and pressure, into electrical signals. They play a pivotal role in applications like automation, robotics, and IoT devices. Photocells, accelerometers, and temperature sensors are just a few examples of the sensor.
Resonators and Oscillators: Generally, resonators and oscillators generate stable frequencies for timing purposes in electronic systems. Quartz crystals, ceramic resonators, and crystal oscillators are common components used for frequency control.
Connectors: Connectors create the physical and electrical connection between different parts of a circuit or between devices. USB connectors, HDMI connectors, and VGA connectors are examples of widely used connectors.
Transformers: Power transformers transfer electrical energy between circuits through electromagnetic induction. Inside a circuit, there are different levels of voltage needed. By the same transformer, different level control voltage can be sent for circuit different operations.
Navigating the vast landscape of electronic components is a rewarding journey for those eager to delve into the world of electronics. Whether you're a hobbyist experimenting with circuits or a professional designing cutting-edge technology, a solid understanding of electronic components is the key to unlocking endless possibilities in this ever-evolving field.