What is Control Valve and its Classifications
A valve with a pneumatic, hydraulic, electric, or other externally powered actuator that automatically opens or closes the valve fully or partially by signals received from controlling instruments is called a control valve.
Control Valve has been used since the day of modernization. This type of valve is mainly used in various industrial sectors where the flow of air or liquid must be controlled. Control valve comes in multiple shapes and sizes that are specifically designed for specific needs. A control valve has two parts. The first one is an actuator that can be actuated by a Pneumatic signal (0-10VDC / 4-20mA) or external force by any other liquid or air.
Definition of Control Valve: A valve with a pneumatic, hydraulic, electric, or other externally powered actuator that automatically opens or closes the valve fully or partially by signals received from controlling instruments is called a control valve.
Functions of Control Valve: The control valve controls fluid flow to control other process parameter such as pressure, temperature, level, flow, etc. A control valve functions as a variable resistance in a pipeline. The control valve directly controls the fluid flow and because of that it is called the final control element.
Classification of Control Valve:
Classification Based on Operating Power:
- Pneumatically operated control valve
- Electrically operated control valve
- Hydraulically operated control valve
Pneumatically operated control valves are most popular in use for reliability and effective control.
Classification Based on Valve Body and Construction:
- Glove valve
- Butterfly valve
- Diaphragm (Saunders) valve
- Angle valve
- Three-way valve
- Ball/Rotary valve
Classification Based on Control Action:
- Signal to Open: It is called a normally closed (NC) control valve. It closes at 0.2 kg/cm2 and opens at 1 kg/cm2.
- Signal to Close: It is called a normally open (NO) control valve. It closes at 1.0 kg/cm2 and opens at 0.2 kg/cm2.
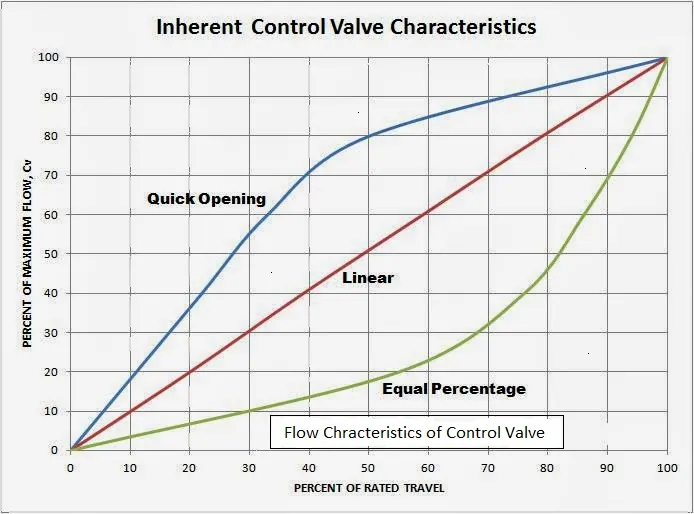
Classification Based on Flow Characteristics:
- Linear flow characteristics control valve
- Quick opening flow characteristics control valve
- Equal percentage flow characteristics control valve
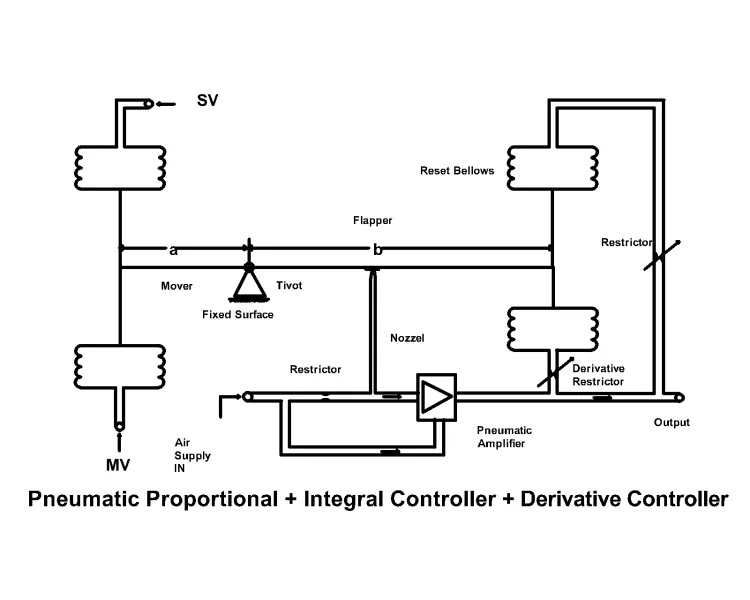
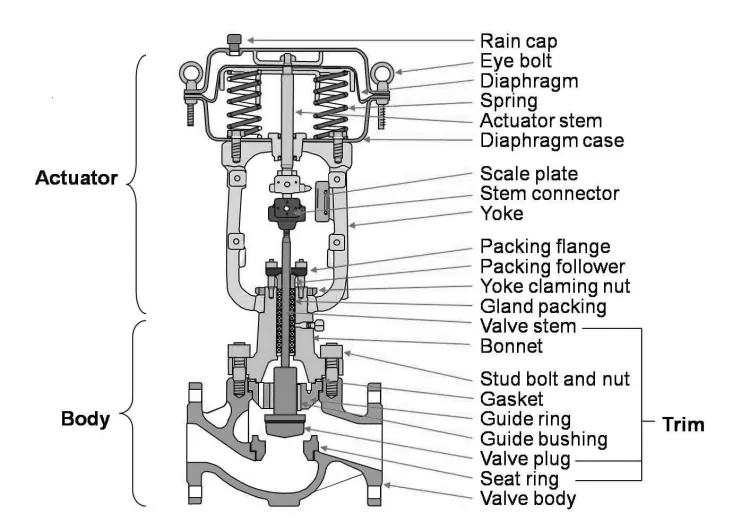
Different Parts of a Pneumatic Control Valve:
The main parts of a pneumatic control valve are the following:
- Valve Actuator
- Valve Body
- Valve Bonnet

Valve Actuator: The valve actuator is operated by a controller signal. The function of the actuator is to open or close the control valve appropriately by using the signal that comes from the controller. Sometimes, control valves are operated manually. In that case, a hand wheel is associated with an actuator. The valve is closed or opened as per the requirement with the help of the hand wheel
Related: Introduction to Distributed Control System (DCS)
Different types of Actuators:
Actuator Based on Action:
- Direct acting actuator: Input increases, actuator stem moves outward.
- Reverse acting actuator: Input increase, actuator stem moves inward.
Piston Cylinder Actuator:
Piston cylinder actuators can be of two types:
- Single-acting cylinder with spring
- Double-acting cylinder without spring
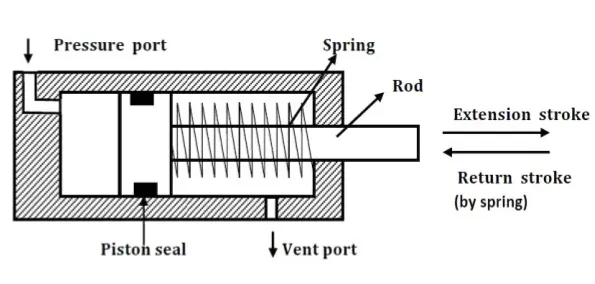
Single Acting Cylinder
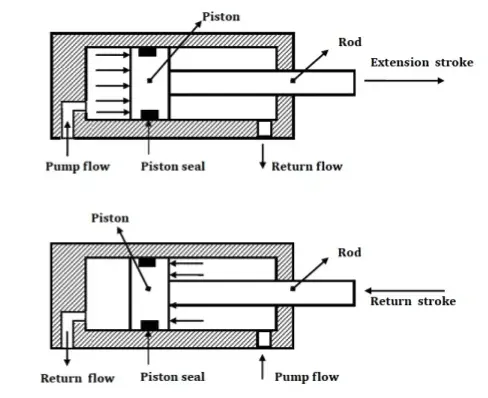
Double Acting Cylinder
Valve Body: The valve body always depends on its application, class, place where it will be installed, etc. There are two classes of control valves
- Linear Motion
- Rotary Motion
Valve Bonnet: A control valve bonnet covers the opening on top of a valve body. As a pressure-retaining part of a valve, the bonnet and its connection to the body are exposed to the operating fluid. As a result, they must withstand the operating pressure and corrosive effects of the fluid.