Industrial Chillers: An In-depth Overview of Cooling Systems in Manufacturing
Industrial chillers are robust cooling systems designed to regulate temperatures in various manufacturing processes where floor temperature directly impacts overall processes like machinery also product quality.

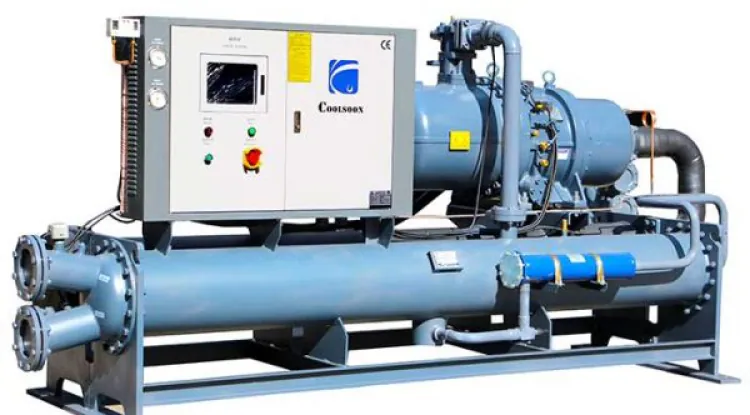
In the intricate dance of manufacturing processes, maintaining optimal temperatures is a critical factor for efficiency and product quality like in the pharmaceuticals, food, and textile industries. Industrial chillers emerge as unsung heroes, providing the cool composure needed to keep production lines running smoothly and also keep machines and humans in good working conditions. Let's take a deep dive into the world of industrial chillers and unravel the complexities that make them indispensable in the realm of manufacturing.
The Chilling Basics:
Industrial chillers are robust cooling systems designed to regulate temperatures in various manufacturing processes where floor temperature directly impacts overall processes like machinery also product quality. Whether it's cooling equipment, materials, or entire facilities, these machines play a pivotal role in preventing overheating, ensuring product consistency, and prolonging the lifespan of machinery. When you have installed the Chiller System then you don't need to worry about the weather outside of your production floor.
Types of Industrial Chillers:
Diversity reigns supreme when it comes to industrial chillers. From air-cooled to water-cooled, absorption to centrifugal, each type caters to specific requirements for different industrial specific needs. Air-cooled chillers, for instance, are more space-efficient and suitable for smaller setups, while water-cooled counterparts offer higher efficiency and are ideal for larger industrial applications like Pharmaceuticals and Textile sectors.
The Inner Workings: Components and Processes
Within the heart of an industrial chiller, a series of different components work in harmony. Compressors, condensers, evaporators, and refrigerants collaborate to absorb, transport, and release heat, creating a continuous cycle of cooling. The efficiency of these components always determines the chiller's overall performance, making them crucial to the reliability of the cooling system. You can read this article where you will get a Chiller Working Principle Steps with examples.
Applications Across Industries:
The applications of industrial chillers span a multitude of industries. From Textile manufacturing and food processing to pharmaceuticals and data centers, these cooling systems cater to diverse needs. Maintaining precise temperatures is particularly vital in sectors where product quality, safety, and regulatory compliance are paramount.
Energy Efficiency and Sustainability:
As the world focuses on sustainable practices, industrial chillers are evolving to meet stringent energy efficiency standards. Smart technologies, variable speed drives, and environmentally friendly refrigerants are becoming integral to modern cooling systems. Different brands are continuously working on the development of their existing product into more advanced products. Manufacturers are increasingly adopting eco-friendly approaches to not only comply with regulations but also reduce operational costs in the long run.
The Human Factor: Expertise in Chiller Operation and Maintenance
While technology drives industrial chillers, the human touch is equally crucial. Because several issues will arise when the Chiller is not operated in good hands. For this reason, skilled operators and maintenance personnel ensure that chillers operate at peak performance. Regular inspections, preventative maintenance, and swift troubleshooting contribute to the longevity and efficiency of these vital cooling systems. If there is any fall in a chilling system then it will be a serious issue for the machine and humans. For example, if the chilling system falls in pharmaceuticals then the temperature variation can weast a batch of medicine from the process line.
Industrial chillers are the silent guardians of modern manufacturing, maintaining the delicate balance of temperatures in a myriad of processes. Their versatility, efficiency, and adaptability make them indispensable in an ever-evolving industrial landscape, where precision and reliability are the keys to success.