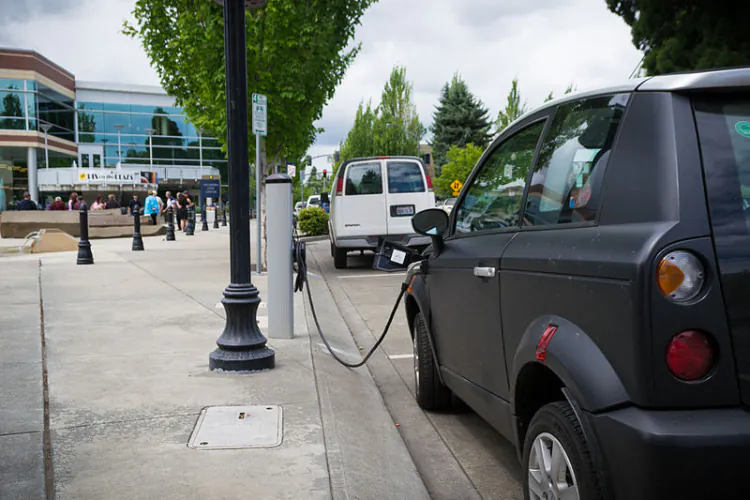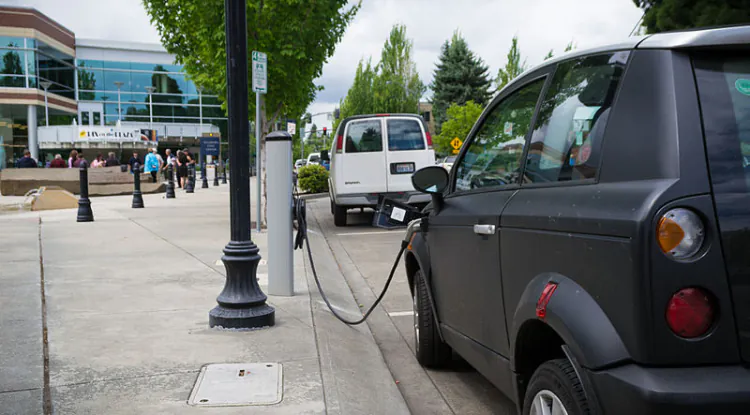General Question About Electric Vehicles
How Electric Vehicles Work, How Carbon-Friendly Are Electric Vehicles & How Far Can You Go?
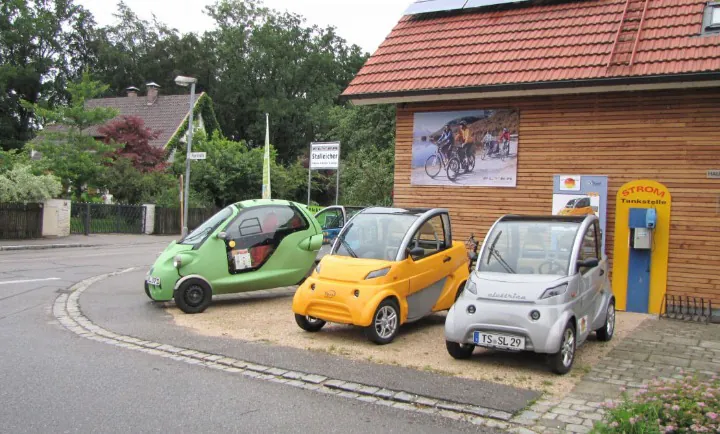
Nowadays’s Battery Electric Vehicles (BEVs) are becoming very popular. Most of the world-renowned companies are inventing and designing more suitable and efficient vehicles that have never been seen before. Several Americans question simply however these electrical eccentricities propel themselves on therefore expeditiously and noiselessly. In this article, I will give you some basic ideas about Electric Vehicles, how Electric Vehicles work, efficiency, and environmental effects.
How Electric Vehicles Work?
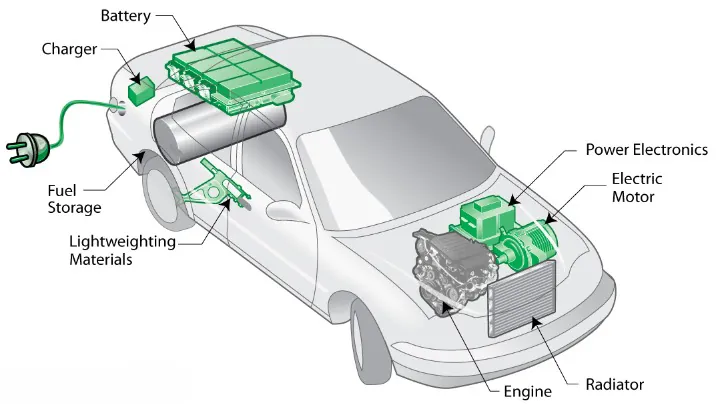
By the name we can understand, that electric vehicles work by using power stored in batteries. The regular car has an engine that runs on liquid fuel or GAS. But in Electric Vehicles a large group of batteries are packed together and they power an electric motor, which turns the wheel of the car.
Just consider your cell phone, over time batteries are depleted and require a recharge. There are no emissions in a BEV, negating the need for smog checks and it doesn’t have a tailpipe. Acceleration response (torque) on electric cars is nearly instantaneous. Rapid pedal response and zippy maneuvering into traffic compared to conventional vehicles. BEVs have few moving parts and they’re also cheaper to maintain, requiring no engine oil changes.
How Carbon-Friendly are Electric Vehicles?
Carbon-friendliness for BEVs depends on the source of electricity that you are using to charge your electric vehicle. Electric vehicles easily powered by electricity from even the dirtiest coal-fired power plants still run more efficiently. These types of power plants produce less pollution than their gasoline or diesel-fueled counterparts. Our regular internal combustion engine car does not have any smoke filter and burned gas can easily be mixed with air. But in power plants, they use smoke filters that reduce the carbon emanation before flue gas relies upon air.
Electrical Vehicles Can Charge by Your Home Outlet Charging:
Electric vehicles can be charged either from a regular outlet in your home or special rapid charging stations when you are out and about. Electrical Vehicles draw much electricity. For this reason, electrical panels and electrical service lines need to be upgraded in older homes. It will ensure safe and efficient charging alongside the smooth operation of other home appliances that are plugged into your home’s electrical system.
Power Regeneration or Savings:
When we drive any car, that time braking is a very common driving activity. In Electric Car braking systems are designed to reuse the kinetic energy created when stopping or slowing the car and using it to recharge the battery. This process is called ‘regenerative braking.’ Modern electric vehicles are also designed to minimize wasted energy, turning the car off when stopped in traffic. Some electric vehicles have solar charging systems.
How Far Can You Go by Electric Vehicles?
It is roughly estimated, that an overnight 8 to 12-hour charge on a standard 120-volt (AC) outlet can push BEVs an average of 70 to 100 miles. Some models can go as far as 265 on a single charge and after that, they need a recharge.
Generally, a BEV owner's home is the primary place for recharging. But restaurants, office buildings, and ‘gas’ stations are becoming a better place for recharging. It will be a rapid charging station roadside. These include ‘AC level 2’ charging stations which use a larger 240-volt AC plug for a faster between 3 to 6-hour charge and ‘DC fast charging,’ which can repower a vehicle in as little as 20 to 40 minutes. If this type of charging facility is installed more on the roadside, then the use of BEV will increase.
Now if you want to get more articles like this then subscribe to our newsletter and don’t forget to share with your friends. Thanks!